Nowadays, Keto and Low-Carb diets are getting lots of attention from fitness enthusiasts especially when they are working out. While the two may seem identical, they are different in structure. Simply put, Keto diets are low-carb in nature, but not all low-carb diets are considered Keto diets. A diet must be high on the “good fats” while having low enough carbs to be called a Keto diet. Today, let’s dive deeper into the difference between the Keto and the Low-Carb diet.
What Is The Keto Diet?
A Keto diet is a type of low-carb diet where the majority of a person’s calorie intake consists of healthy fats and protein and fewer carbohydrates. Typically, the Keto structure requires a person’s daily calorie intake to be at around 70 to 80 percent fat (good and healthy fats), 15 to 30 percent protein and the rest goes to carbohydrates (usually as low as 20 grams, but not higher than 50 grams per day).
Eating less than 50 grams of carbs daily will run the body out of the immediate fuel (glucose) it can quickly use. Glucose is the type of sugar we get from foods, which the body converts to give us energy. As this sugar gets through the bloodstream to the cells, it becomes the blood sugar or glucose. In about 3 to 4 days, the body will start to enter Ketosis, a metabolic state in which the body breaks down protein and fat for energy instead of glucose, making a person lose weight.
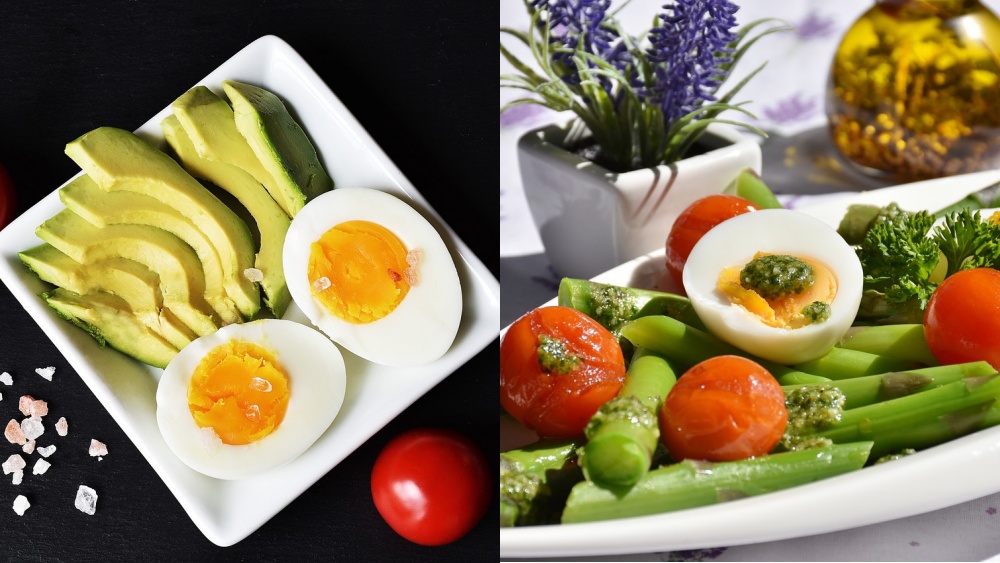
This means the body will burn the available carbs much faster (as well as the glucose/blood sugar) and instead use the fat to produce ketone molecules. A Keto diet plate may look like consuming foods high in good fat and protein such as fish, meat, leafy vegetables, poultry products like eggs, and some olive oil and butter into the mix. On the other hand, taking foods high in carbohydrates like pasta, potatoes, bread, cereals, and others is discouraged.
Take note that the Keto diet is a type of short-term diet (rather than for longevity) that is focused on immediate weight loss rather than on health benefits. Also, building muscle while on a Keto diet can be difficult due to the lower protein intake. Keep in mind that this diet is not advisable for people who are pregnant, lactating, or have health conditions, and it’s always best to consult a doctor and dietitian before giving it a go.
What Is The Low-Carb Diet?
Basically, any diet or eating style consisting of less than 45% of the calories from carbohydrates can be considered a low-carb diet. However, according to different research studies, low-carb diets consist of between 10 and 25 percent of the calories from carbohydrates. An intake of 50 to 150 grams of carbs per day is enough to qualify as a low-carb diet.
Normally, a low-carb diet requires you to take foods rich in protein with some fat rather than the usual way of filling the calories with carbohydrates. While planning the distribution of the calories may vary from one person to another, a typical low-carb diet may look to feel the calories ranging from about 10 to 45 percent from carbs, 40 to 50 percent from protein, and the remaining about 30 to 40 percent is allocated from fats.
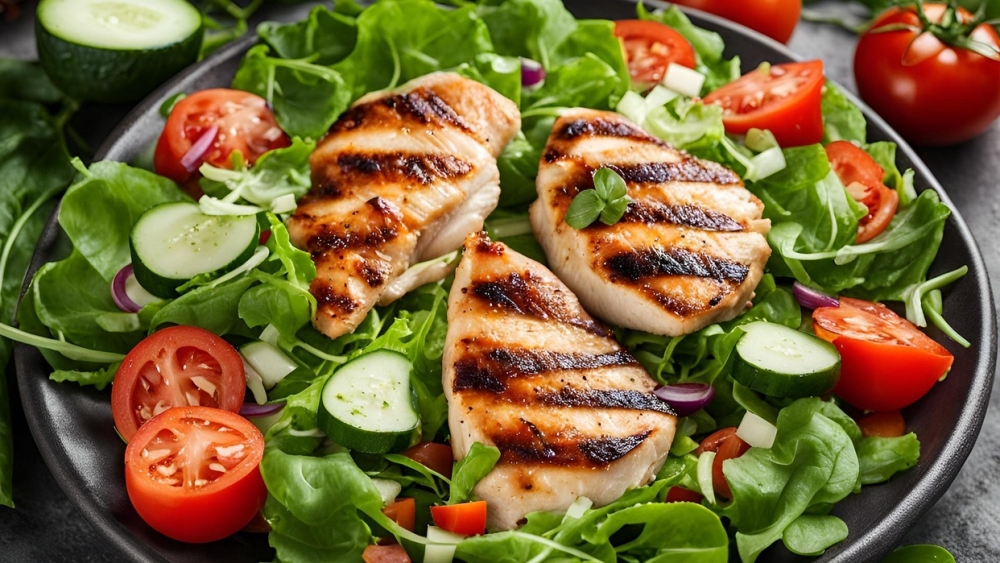
People on a low-carb diet increase their protein intake alongside healthy fats by limiting or not eating foods or beverages high in sugar, pasta, grains, and bread. The big emphasis on protein provides energy and allows a person to maintain muscle mass, as some of the protein may be used for glucose production to provide energy.
In the long run, the low-carb diet is easier to maintain but is less likely to produce immediate results as with the Keto diet.
The Difference Between Keto And Low-Carb Diet
The difference is the stricter scope on which each diet focuses. In a Keto diet, a strict limitation on the amount and type of carbs a person takes is heavily considered. Doing so forces the body to enter Ketosis, a metabolic state in which the body produces ketones by breaking down protein and fat to provide fuel instead of glucose. This type of diet focuses on intaking proteins and good fats (poultry, meat, seafood, nuts, and seeds) and a lot less on carbohydrates.
On the other hand, the low-carb diet is a more general approach that refers to a person’s overall diet. It limits carbohydrate intake but is not as strict as the Keto diet. It encourages removing low-quality carbohydrates such as processed foods, sugars, pasta, and grains.
While the two diet terms are often used interchangeably, they are very different in terms of the macronutrient (fat, protein, and carbohydrate) breakdown. Keto consists of about 5 to 10 percent of the total calorie intake from carbs, about 15 to 30 percent from protein, and 70 to 80 percent from healthy fats, which means that the Keto diet contains about twice as much fat and about half as many carbs compared to the typical low-carb diet.
Entering the Keto and Low-Carb diets is both a good way to lose weight. Generally, people are often advised to first try the low-carb diet before trying the Keto diet for weight loss and better overall health. Due to its restrictive nature, the keto diet may be able to produce quicker results in terms of weight loss, but it may come with consequences, especially for those people who have a health condition.
To put into perspective, some doctors even recommend entering the Keto diet for patients who have cardiovascular diseases, certain types of diabetes, and even Alzheimer’s disease.
Which One’s Better?
Before considering either of the diet types, it is important to first examine the person’s nutritional habits, current health status, and lifestyle. The low-carb diet may be easier to follow in the long run than the Keto diet, as it offers more options and is less strict.
Most of all, it depends on the person’s ability to stay disciplined and focused on the diet. Keto will be able to produce a dramatic and faster weight loss, especially for those who are challenging themselves within a given timeline. Whereas the Low-Carb diet may be better for those people who are looking to decrease their weight sustainably and gradually and want to record their weight loss journey.
It is important to always first seek a doctor as the Keto diet consists of high-fat foods doing so right away can be dangerous, especially for people who have medical conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney damage, those who have gallbladder removal, or nursing or pregnant women.
On the other hand, different studies show that low-carb diets can be better for general health, not just weight loss. These include improved cardiovascular fitness and lower insulin and blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Always consider the type of lifestyle, current fitness level, and health goals when considering a diet. Controlling what we eat is the first step to ultimate self-discipline. See how long you can stick to a diet plan, and soon, your mind and body will follow.
You may also like: